What is HFMD?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, or HFMD, is a contagious illness caused by different viruses. Infants and children under 5 years old are more likely to catch it. But, older children and adults can also get it.
What are the common symptoms of HFMD?
- fever
- loss of appetite
- sore throat
- a feeling of being unwell
- 1-2 days after the fever starts
- painful sores in the mouth
- a skin rash may also develop on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Sometimes rash also appears on the knees, elbows, and buttocks. The rash may blister, but won’t itch.
- Young children tend to drool and avoid swallowing and may refuse to drink or eat because of the discomfort.
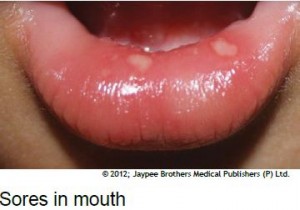
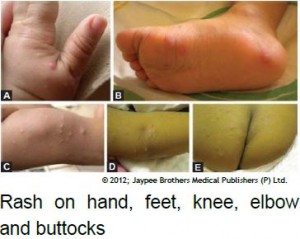
Not everyone will get all of these symptoms. Some people may show no symptoms at all, but they can still pass the virus to others.
How is HFMD Spread?
The viruses that cause HFMD spread very easily. The viruses are found in an infected person’s saliva, mucus (cold), feces (do-do); and in the fluid of their blisters.
You or your child may catch it by:
- close contact, such as kissing, hugging, or sharing cups and eating utensils with people who have HFMD
- being near someone with it who sneezes or coughs
- touching unwashed hands
- touching surfaces handled by infected persons who didn’t wash their hands after sneezing or coughing in them, or using the bathroom. contact with feces (do-do) for example when changing a diaper contact with blister fluids
How to prevent HFMD and keep your children safe?
Wash hands often with soap and water:
- after using the toilet
- after changing a diaper
- before eating
- before preparing meals
- after handling a sick person
Avoid:
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth with unwashed hands.
- Avoid close contact such as kissing, hugging, and sharing cups and eating utensils with people who have HFMD.
Clean toys surfaces often
Clean with soap and water and then disinfect with bleach solution.
Keep sick children out of school or day care
Sick children should be kept out of school or child care for a few days to avoid spreading the germ.
Treatment for HFMD
There is no specific treatment for hand, foot, and mouth disease. Managing the fever and preventing dehydration are the primary goals. However, any high fever in a very young infant must be evaluated by a health-care practitioner. For older infants and children, as long as the child is drinking lots of fluids, they may be comfortably monitored at home.
Home Care
Paracetamol may be used to help relieve fever and pain.
Do NOT take aspirin, or other pills containing aspirin.
Avoid acidic fluids, like orange juice. as they may irritate sores in the mouth.
Seek immediate medical attention if:
- your child has fever for more than 24 hours, or
- your child develops any signs or symptoms of dehydration
Young children, may get dehydrated if they are not able to swallow enough liquids because of painful mouth sores.
Signs of Dehydration
- dry skin
- dry nostrils or lips
- weight loss
- constantly fussy
- lack of usual energy
- less urine (pee pee) than usual
When in doubt, contact your child’s health-care provider.
